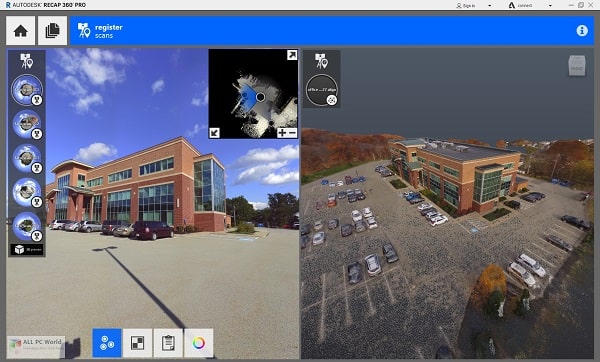
Photogrammetry software plays a crucial role in image enhancement by transforming 2D photographs into detailed 3D models. This technology is widely used across various fields, including architecture, archaeology, gaming, and virtual reality. Here’s a breakdown of how photogrammetry contributes to image enhancement.
1. High-Quality Model Creation
Photogrammetry software analyzes multiple images of a subject taken from different angles. By identifying common points in these images, it constructs a high-resolution 3D model. This process captures intricate details that enhance the overall quality of the visual representation.
2. Improved Detail and Accuracy
Through techniques like dense point cloud generation, photogrammetry can create highly detailed models. The software processes images to provide accurate spatial measurements and textures, resulting in a more realistic representation of the subject. This level of detail is essential for applications that require precision.
3. Texture Mapping
One of the key features of photogrammetry software is its ability to apply textures derived from the original images. By mapping these textures onto the 3D model, the software enhances the visual fidelity. This results in more lifelike appearances, as colors and surface details are accurately represented.
4. Reduction of Visual Artifacts
Photogrammetry software often includes tools for cleaning up visual artifacts that may occur during the image capture process. This helps eliminate issues such as noise, blurriness, or misalignments, ensuring that the final model is of high quality and visually appealing.
5. Post-Processing Capabilities
Many photogrammetry tools offer post-processing features that allow users to refine and enhance their models after initial creation. Users can adjust lighting, textures, and other visual elements to achieve the desired look. This flexibility is vital for preparing models for presentations or further artistic manipulation.
6. Facilitating Visualization and Analysis
In fields like architecture and archaeology, enhanced images and models facilitate better visualization and analysis. Stakeholders can examine intricate details, assess structural integrity, or understand historical contexts, all supported by high-quality visual data.
Conclusion
The role of photogrammetry software in image enhancement is multifaceted, involving the creation of detailed models, accurate texture mapping, and the reduction of visual artifacts. By leveraging these capabilities, professionals across various disciplines can achieve impressive results, enhancing both the aesthetic and functional quality of their visual representations.