Due to the rise of immersive media and better camera equipment, digital artists are reshaping photogrammetry for application in a wide range of industries like leisure, geospatial, medical, etc., and mediums like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), extended reality (XR), and 3D printing.
Do you want to know more about photogrammetry and get the best photogrammetry software? Check out our Beginner’s approach to Photogrammetry to get started.
Photogrammetry: What is it?
The processes of documentation, assessing, and translating photographic images and patterns of observed radiant electromagnetic energy and other phenomena constitute the art, science, and technology of photogrammetry. It is used to obtain accurate information about real-world objects and the environment.
What is the purpose of photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry has a long history of application in geospatial-data-dependent fields like surveying, archaeology, mining, and others. Topographic maps were produced using photogrammetry as early as the middle of the 19th century.
Digital artists now utilize photogrammetry to construct replicas of fixed real-world objects, architecture, and 3D immersive settings due to the growth of virtual characters and better camera technology.
How does Software for Photogrammetry Operate?
With photogrammetry software, 3D models can be enhanced, edited, and optimized by artists and designers for use in architecture, video games, movies, and other projects. Various specialized software tools may be used in this procedure, depending on the workflow and desired project outcome.
How can I begin using photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry can be done with very minimal equipment. To get started, all you need is a camera (a smartphone will also do), a PC or Mac, photogrammetry processing software, and 3D editing tools. Depending on what you’re photographing, where you’re photographing it, and when you want to photograph it, additional equipment like lighting, filters, and lenses can also be required.
Tips and Procedures for Photogrammetry
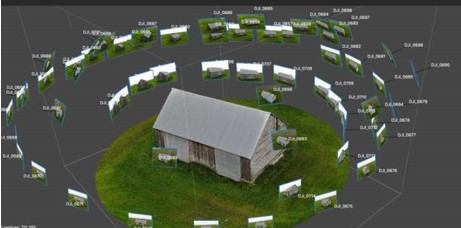
An overly straightforward photogrammetry procedure can be divided into two primary components. Please be aware that a simple photogrammetry workflow is difficult to define. The procedure is heavily influenced by the item you’re photographing, how you intend to utilize the digital item, the software you intend to use, and other factors.
Capture: The initial stage in photogrammetry is to precisely capture the item from a variety of overlapping viewpoints.
- What am I recording, and how will it be used in the finished product? Is it a forensic video? Mind you, It can be difficult to catch items that are moving, flashy, or reflective.
- Where will I be taking photos? Find a place that is quiet and big enough to photograph your subject.
- When will I be taking pictures? Wind, rain, and snow are examples of environmental elements that might generate movement or reflections. Strong shadows and hotspots caused by harsh sunshine can hinder editing.
Processing: Post-processing, which is what you do after you’ve rebuilt your item, frequently entails mesh generation, compression, color correction, manual editing, visualization, and other things.
Best Photogrammetry Software to Use Today
As a general set of forensic photogrammetry software tools, Cognitech AutoMeasure is the best photogrammetry program to use for evaluating data from video or image evidence. The benefit of using this software is that it can essentially measure any dimension in the clearly visible crime scene, including vehicle components, biometric body dimensions other than height (such as shoulder width), scene lengths, angles, and areas, in addition to measuring the subjects’ height, which the rival can also do in some specific circumstances.